WSB3-20, WSB3-20H
Wall switch button, 2 buttons
Overview
An overview of the product design and usage. Also contains circuit diagrams, terminal details, etc.,
Key Features
Wall controllers with low-upstroke control WSB3-20 and WSB3-20H are the main and most frequently used units (controller) in the iNELS system.
Model Variants:
The WSB3-20 and WSB3-20H are wall controllers available in a 2-channel version.
Both models feature built-in micro-buttons with a low upstroke, offering elegant and easy control.
LED Indicator: Equipped with a double-color (red/green) LED diode to indicate the status of controlled appliances or sensors/actuators in the system.
Compatibility: WSB3 series wall buttons are compatible with LOGUS90 frames (85.6 x 85.6 or 94 x 94 mm), allowing for combination with double and triple frames and other classic products of the series.
Sensor and Inputs:
Each controller is equipped with a temperature sensor.
Two analog/digital inputs (AIN/DIN) are available, which can be used to connect potentialless contacts or an external temperature sensor (TC/TZ) (e.g. for measuring floor temperature).
WSB3-20H Additional Features:
WSB3-20H includes a relative humidity meter.
Can be used with 99621T including accessories 99622 (Vista MT) and 99,623 (Vista IRMT), for better access of air to the sensor instead of the housing cover 99601T.
Functionality of WSB3-20H
Compared to standard wall buttons WSB3-20H, Offers flexibility and multifunctionality.
Supports various control methods, including short and long push for controlling appliances (e.g., dimming, shutter control, scenes).
Control Modes: Each button (fold) can have different functional modes besides lighting control, including:
Classic wall-switch: - upper button ON, bottom button OFF
Button controller (impulse relay): - first press ON, second press OFF.
Dimmer: - short press – ON/OFF.
Time switch: - ON after press, automatically OFF after set time.
Setting light scenes – example: for watching TV: - shutters down - main light 30% intensity - wall-lamps 50% intensity
Each button can control any appliance in the system and can use a variety of centralized or time-controlled features. Accordingly, the customer can choose the simplicity/complexity of the operation. The big advantage is the possibility to changing the method of control by only making software modifications without physical interventions into the structure of the building.
Mounting: Designed for mounting into an installation box, particularly suitable for LOGUS90 design.
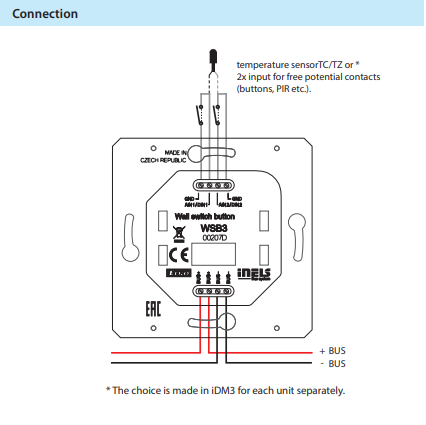
Exemplary circuit diagram/ Wiring Diagram
Compatibility chart ( CU, minimal FW version and Integration)
The chart illustrates the compatibility between wall switch button and various central units, firmware versions, and integration options.
1
CU3-01M
01.36.00/02.84.00
NA
NA
2
CU3-02M
01.36.00/02.84.00
NA
NA
3
CU3-07M
04.00.00
Yes
Yes
4
CU3-08M
04.00.00
Yes
Yes
6
CU3-09M
Preparation
Preparation
Preparation
7
CU3-10M
Preparation
Preparation
Preparation
Programming in iDM
Introduction
iNELS Design Manager, or IDM3, is for programming iNELS units. This software serves as the platform for configuring device parameters, defining functions, and executing the programming required for iNELS units.
Device parameters, such as sensor range and thresholds, backlights, and operational modes, can be easily adjusted within the IDM3.
The process of programming in IDM3 typically involves defining functions and establishing logical connections between different devices. This allows for the creation of automation scenarios and the implementation of intelligent control strategies.
Starting up
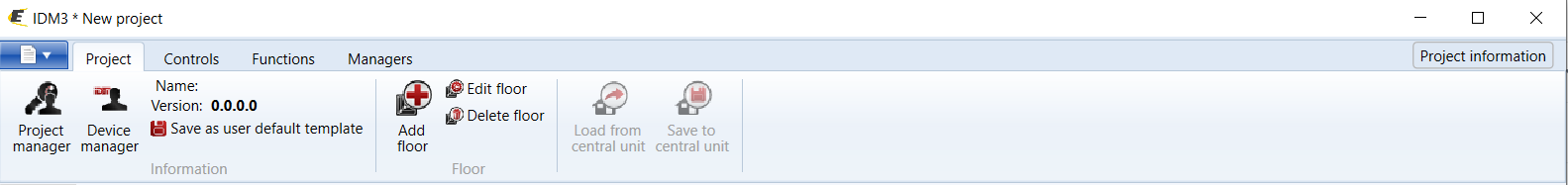
Select the "blue control icon" as shown in Fig 1 > Clicking on the option "New project from default template“ allows you to create a new project from a predefined template.
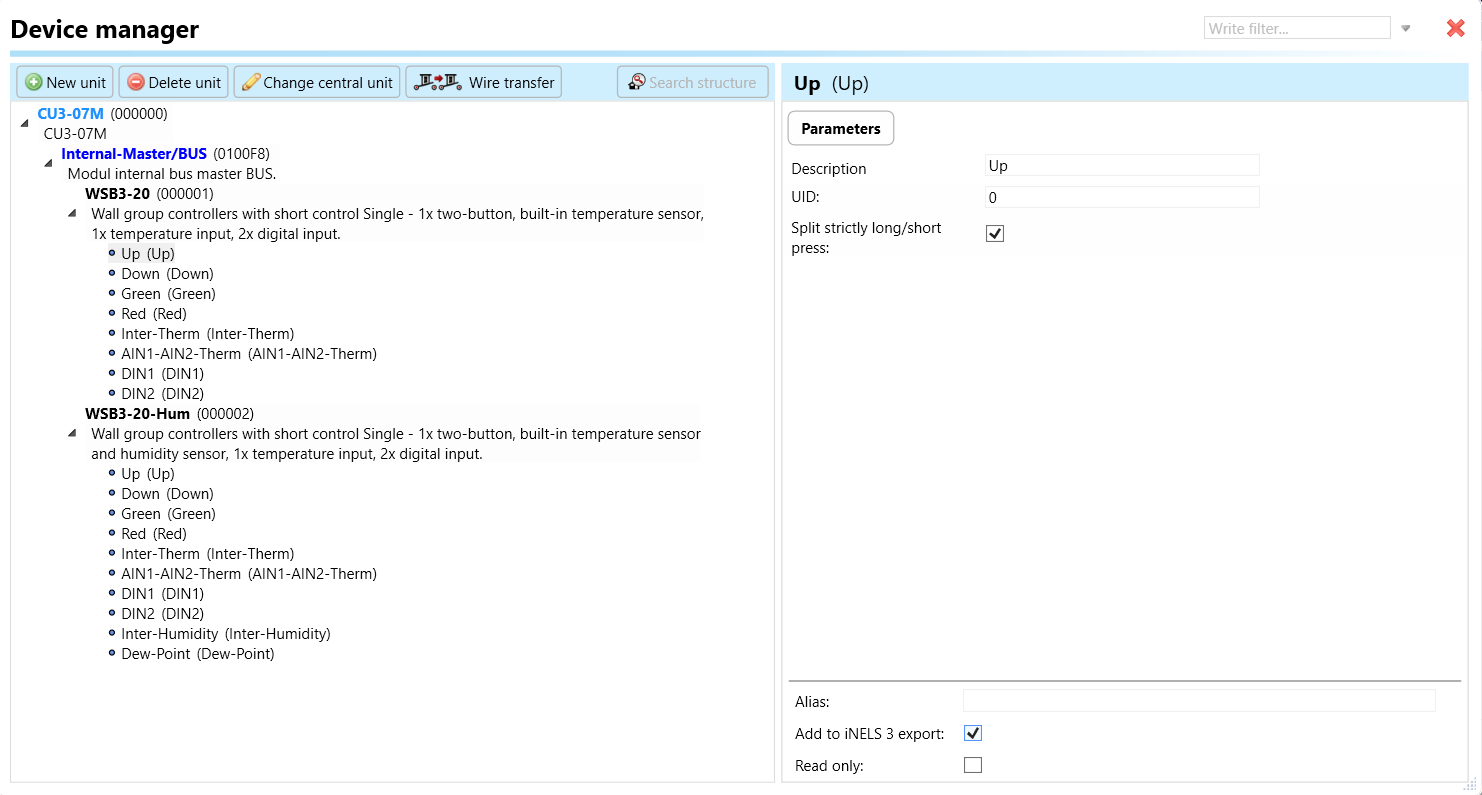
Select the "Device manager" (Fig 1)> Add "New unit "> Select the central unit > Add "New unit">Select the "Internal-Master/ BUS"> Add "New unit "> Add the devices> Click on the devices to see the "Parameters".
Parameters:
Parameters in the iNELS devices refer to the measurable factors or characteristics that define the behavior or performance of the device. These could include electrical properties, physical dimensions, environmental conditions, and various other specifications depending on the type of device.
These are settings specific to individual devices within your automation system.The specific parameters of the WSB3-20, WSB3-20H in the iDM as shown in Fig.2
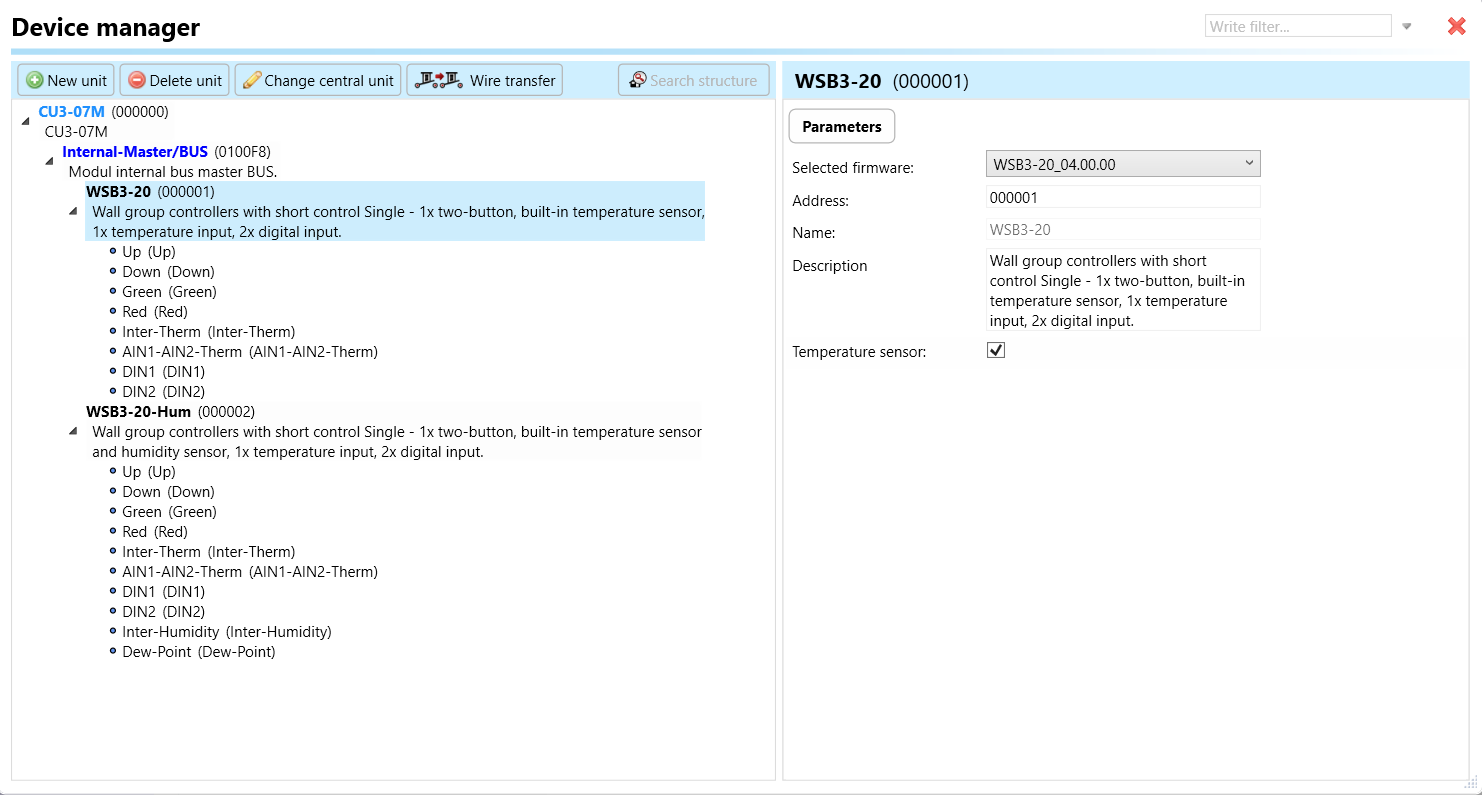
Clicking on the WSB3-20, WSB3-20H (Fig.2), will navigate to the selected firmware, address, name, and description, along with other parameters as described below:
Temperature sensor: The temperature sensor is a built-in component of the WSB3-20H controller. It facilitates temperature measurement and monitoring within the immediate vicinity of the wall controller.
WSB3-20 parameters:
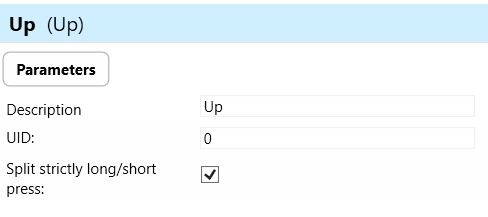
Up:
The "Up" parameter refers to the upward button or action on the wall controller. The "Up" button may be used for various purposes depending on the configuration or programming of the wall controller.
The set of actions in SW “ short press, short release, long press, long release, and permanent action can be used with various functions.
Down:
The "Down" parameter refers to the downward button or action on the wall controller. The "Down" button may be used for actions such as decreasing brightness, lowering blinds, or triggering specific scenes, depending on the configuration or programming.
The set of actions in SW “ short press, short release, long press, long release, and permanent action can be used with various functions.
Green: The "Green" parameter refers to the green LED indicator on the wall controller. This LED may illuminate to indicate certain statuses or conditions, such as the device being ON or specific functions being active.
Red: The "Red" parameter refers to the red LED indicator on the wall controller. Similar to the "Green" parameter, it indicates specific statuses, conditions, or functions through illumination. The red LED provides visual feedback to users, likely device OFF or inactive states.
Inter-Therm:
The "Inter-Therm" parameter refers to the inter-thermal functionality or capability of the wall controller, possibly related to temperature monitoring or control.
Inter-Therm functionality may allow the wall controller to interface with temperature sensors or systems, enabling temperature monitoring, regulation, or integration with HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.
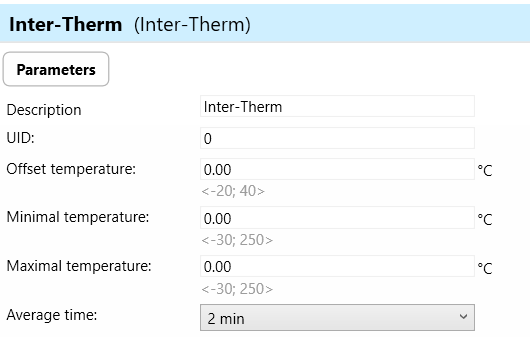
a) Offset Temperature: Offset temperature refers to a user-configurable adjustment applied to the temperature readings from the connected sensor. It allows users to compensate for any systematic errors or inaccuracies in the temperature measurements.
b) Minimal Temperature: This parameter defines the minimum acceptable temperature value that the device can measure or handle. It sets a lower limit to ensure that temperature readings below this threshold are considered valid and within the device's operating range.
c) Maximal Temperature: Similar to minimal temperature, the maximal temperature parameter sets the maximum acceptable temperature value that the device can measure or handle. It establishes an upper limit to ensure that temperature readings above this threshold are considered valid and within the device's operating range.
d) Average Time: Average time refers to the duration over which the temperature sensor integrates or averages multiple readings to calculate a representative value. This parameter helps to smooth out fluctuations in temperature levels.
AIN1-AIN2-Therm (Analog/Digital Inputs 1-2 for Temperature):
AIN1-AIN2-Therm refers to the analog/digital inputs specifically designed for connecting temperature sensors (e.g., TC/TZ sensors) to the wall controller.
These inputs facilitate temperature monitoring and control, allowing the wall controller to receive temperature readings from external sensors and respond accordingly.
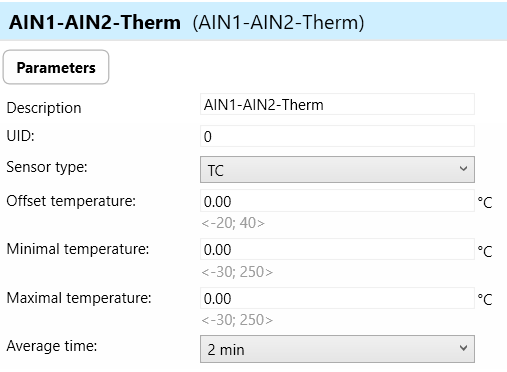
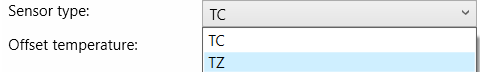
a) Sensor type: There are two types of sensor namely, TC and TZ.
b) Offset Temperature: Offset temperature refers to a user-configurable adjustment applied to the temperature readings from the connected sensor. It allows users to compensate for any systematic errors or inaccuracies in the temperature measurements.
c) Minimal Temperature: This parameter defines the minimum acceptable temperature value that the device can measure or handle. It sets a lower limit to ensure that temperature readings below this threshold are considered valid and within the device's operating range.
d) Maximal Temperature: Similar to minimal temperature, the maximal temperature parameter sets the maximum acceptable temperature value that the device can measure or handle. It establishes an upper limit to ensure that temperature readings above this threshold are considered valid and within the device's operating range.
e) Average Time: Average time refers to the duration over which the temperature sensor integrates or averages multiple readings to calculate a representative value. This parameter helps to smooth out fluctuations in temperature levels.
DIN 1, 2 (Digital Inputs 1, 2):
DIN 1, 2 refer to the digital inputs on the wall controller, which can be used to connect external devices or sensors with potential-free contacts, such as switches, buttons, alarms, or detectors.
These inputs enable the wall controller to receive signals from external devices or sensors, allowing users to trigger specific actions or functions based on input events.
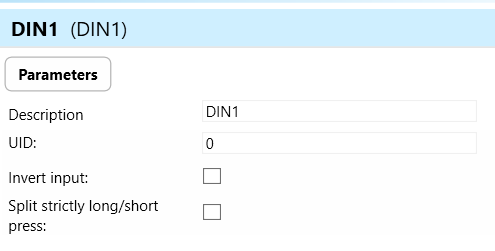
Invert Input: Invert input refers to a configuration setting that reverses the logic state of a digital input signal. When "Invert input" is enabled for a specific digital input channel (DIN) on the device, it means that the logical interpretation of the input signal is inverted.
For instance, if a digital input channel is normally interpreted as "active" when the input signal is high (logic level 1), enabling "Invert input" would cause the channel to be interpreted as "active" when the input signal is low (logic level 0), and vice versa.
Split Strictly Long/Short Press of DIN: Split strictly long/short press of DIN is a feature that distinguishes between short and long press actions on a digital input channel (DIN).
Short press actions typically trigger immediate responses or commands, while long press actions may initiate different or additional functions after a predefined duration.
WSB3-20H parameters:
Inter-Humidity: "Inter-Humidity" refers to the internal humidity sensor integrated into the WSB3-20H device. It measures the relative humidity in the environment.
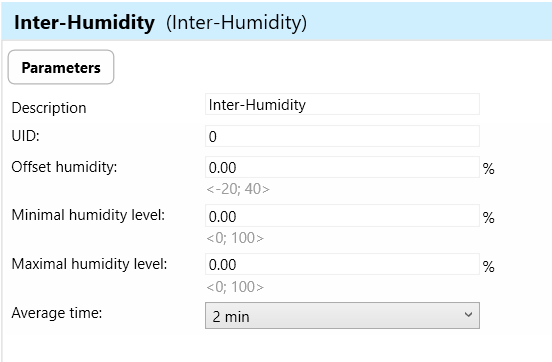
Offset Temperature: Offset temperature refers to an adjustment applied to the humidity readings to compensate for temperature variations that may affect the accuracy of humidity measurements. This adjustment ensures that humidity readings remain accurate and reliable across different temperature conditions.
Minimal Humidity Level: Minimal humidity level refers to the lowest threshold at which the WSB3 device will trigger actions or responses based on changes in humidity levels detected by the humidity sensor. When the measured humidity falls below the minimal level, the WSB3 device initiates appropriate actions to maintain or increase humidity levels
Maximal Humidity Level: Maximal humidity level refers to the highest threshold at which the WSB3 device will trigger actions or responses based on changes in humidity levels detected by the humidity sensor. When the measured humidity exceeds the maximum level, the WSB3 device initiates appropriate actions to reduce or control humidity levels.
Average Time: Average time refers to the duration over which the humidity sensor integrates or averages multiple readings to calculate a representative humidity value.
Dewpoint: Dewpoint refers to the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to condensation. The WSB3-20H may have the capability to calculate or measure the dewpoint based on the temperature and humidity data from its integrated sensors.
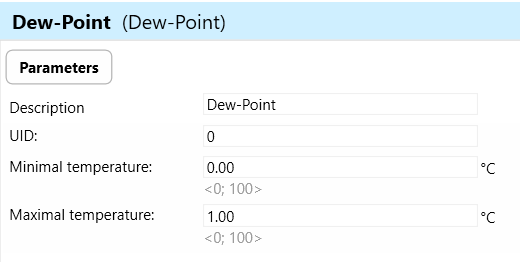
Minimal Temperature: The minimal temperature parameter refers to the lowest temperature at which the integrated temperature sensor of the WSB3 device can accurately measure ambient temperature. This parameter is important because it defines the lower limit of the device's temperature measurement range.
Maximal Temperature of Dew-point: The maximal temperature of dew-point refers to the highest temperature at which dew point, the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture and dew begins to form, can occur. Dew point is influenced by both temperature and humidity, and exceeding the maximal temperature of dew point may lead to condensation or dew formation on surfaces.
Exports for iNELS Cloud and APP
Setting Up Control and Monitoring for iNELS Cloud and iNELS App
It is possible to control and monitor all the bus units in iNELS cloud and iNELS app. There are two stages to set up this function. Stage one is to do configuration in iDM3 and stage 2 is to do Configuration in iNELS cloud page and iNELS app.
Configuration in iDM3.
1. Unit and Parameter Selection:
Begin by accessing the iDM3 interface on your PC connected to CU. Navigate to the Device Manager section and carefully select the units and parameters you wish to control. This step is essential for determining what gets exported to the iNELS cloud and app.
2. CU Configuration and Third-Party Settings :
After the above step, go to the CU configuration in the iDM3, and select the page for third-party settings.
Inside the third-party settings page, designate the port for cloud connection. Set the mode of operation and choose the numerical system as hexadecimal. Pay close attention to verifying and configuring all essential parameters for successful cloud export.
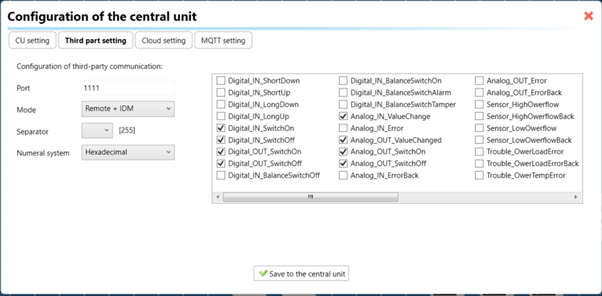
3. Cloud Settings:
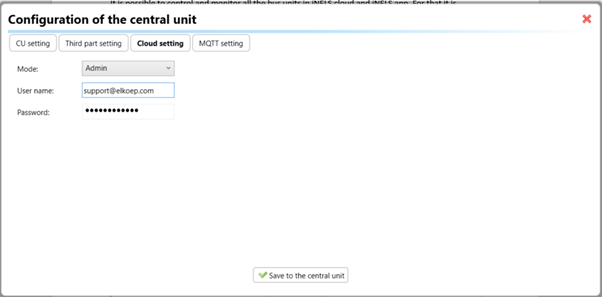
Move on to the Cloud Settings section within iDM3.
Input the details of your iNELS cloud account. If you haven't created one, utilize the "New User" tab on the iNELS Cloud web page to establish a free account. (Inels Cloud - ElkoEP).
Select the mode and input the cloud account credentials. Save the project to the central unit to generate and store the export project file in the iNELS cloud account.
Configuration in iNELS cloud page and iNELS App.
1. Online Status Verification:
Once the cloud credentials and export settings in iDM3 are configured successfully, check the iNELS cloud account's Gateway section. Confirm that the Central Unit (CU) is online and that the export file has been automatically sent to the cloud under your account.
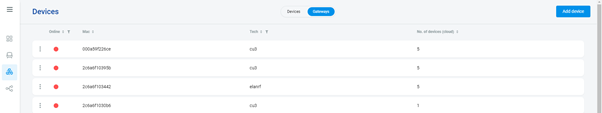
2. Device Creation in Cloud Platform:
In the cloud platform, you have to create new devices in order to control it remotely.
In the device tab, you will find the add device button, which can be used to associate export elements from IDM with the required types and icons.
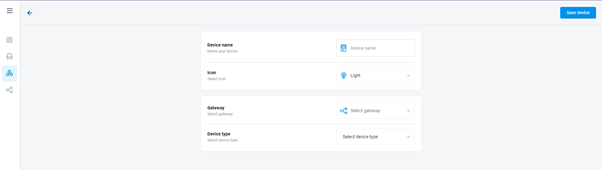
After entering any name of the device, you select the icon, the MAC address of the communication gateway (in this case CU3), a specific type of device and the address of a specific function and element from the iNELS BUS system.
Note: In order to be able to use the iNELS application for communication with CU3 over the local network or the cloud, it is necessary to create a configuration on the website.
Follow these steps meticulously to ensure a seamless configuration process for controlling and monitoring all bus units through iNELS cloud and iNELS app.
3rd Party Integration with iNELS BUS
3rd Party Integration (MQTT)
iNELS units support MQTT integration on central units CU3-07M, CU3-08M, CU3-09M, and CU3-10M. It is necessary to select the devices and parameters for 3rd party integration on the device manager in the iDM.
Please note that you have an MQTT broker (local or cloud) running in the installation for this integration.
After you have a working MQTT broker you need to configure iNELS Central units to communicate with it. If you have no knowledge of what MQTT is, you can learn about it from MQTT Essentials articles. https://www.hivemq.com/mqtt/
There is a pre-installed MQTT broker in the iNLES bridge, it can be used to connect the iNELS Central units for integration in your projects.
Configuration in iDM3: Select units of 3rd Party integration.
Unit and Parameter Selection:
Begin by accessing the iDM3 interface on your PC connected to CU. Navigate to the Device Manager section and carefully select the units and parameters you wish to control. This step is essential for determining what gets exported to the 3rd party integration via MQTT. 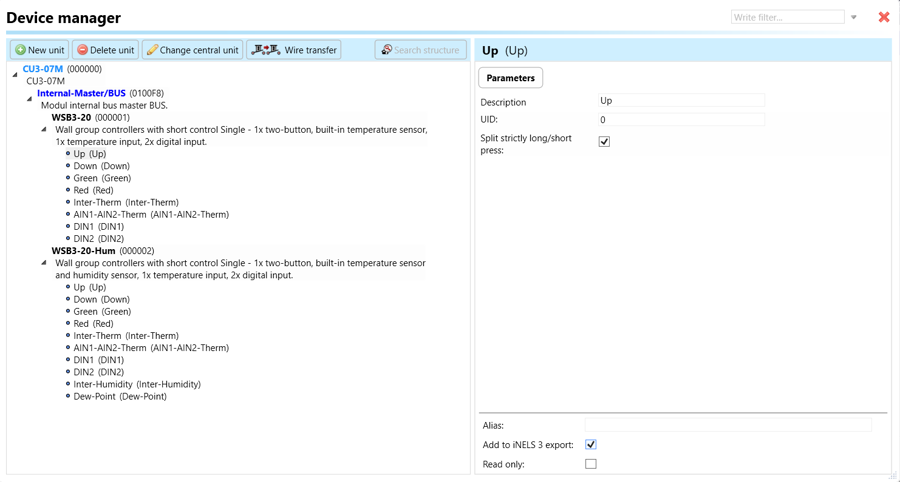
2. CU Configuration and Third-Party Settings :
After the above step, go to the CU configuration in the iDM3, and select the page for third party settings.
Inside the third-party settings page, designate the port for third-party connection. Set the mode of operation and choose the numerical system as hexadecimal. Pay close attention to verifying and configuring all essential parameters for successful third-party integration.

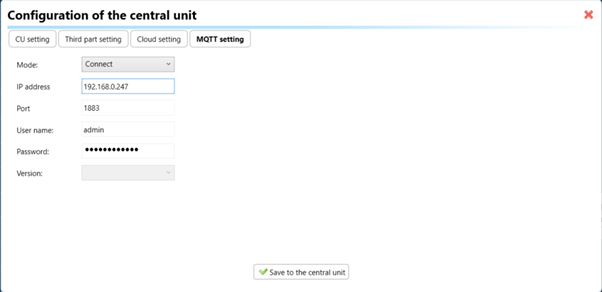
3. MQTT Settings:
Move on to the MQTT Settings section within iDM3.
Input the details of your MQTT broker.
Select the mode and input the broker credentials such as IP, port username and password. Save the project to the central unit.
MQTT payload
Appendices
Provide any optional, supplementary information that may help in providing a more comprehensive understanding of the product feature
Last updated